What Is Algo Trading? A Practical Guide for Retail Traders

Blog by Cirrus.Trade

If you’ve ever followed a repeatable set of rules to place a trade, you’ve already touched on algo trading. At its core, it’s just rules → actions. No magic button. No guaranteed profits. Just a disciplined way to turn a repeatable idea into a consistent workflow.
This guide explains algo trading in plain English, shows how manual and automated approaches complement each other, and outlines a safe, platform-neutral path from signals to execution to review. It’s written for Indian retail traders and is purely educational.
For anyone exploring algo trading in India, this guide simplifies how real traders apply automated trading India workflows - without coding or hype.
What Is Algo Trading in India and How Does It Work?
A plain-English definition of algo trading
Algo trading (algorithmic trading) means using predefined rules to decide when to enter/exit and how to size/manage a position. The rules can be executed by you manually, by software automatically, or by a hybrid of both.In India, algo trading has become increasingly popular. Traders use the best algo trading software to automate stop losses, order placement, and portfolio tracking.
What it isn’t:
- A guarantee of profits
- A way to bypass risk
- “Set and forget” in all market conditions
What it is:
- A way to reduce impulsive decisions
- A way to repeat what works with fewer mistakes
- A way to review trades with evidence (logs)
Whether you run a manual strategy or a fully automated trading India setup, the principle remains: execute rules with discipline.
Manual vs Automated Trading and the Hybrid Reality Most Traders Miss
Most traders assume they must choose: either click everything manually or fully automate. In practice, many consistent traders use a hybrid:
- Manual trading excels at reading context and reacting to nuance. You see the tape, you decide. It’s flexible. The trade-off is discipline and repeatability under pressure.
- Automated execution excels at consistency. Software doesn’t forget to place an SL. It applies the same rules every time. The trade-off is brittleness when the market regime changes and your rules lag reality.
- Hybrid flow = use manual discretion for entries and automated rules for the parts humans often mess up: risk caps, SL/TP templates, partial exits, and logging. You keep judgment where it matters and automate the chores that require perfect consistency.
This hybrid approach is the core of modern algo trading India platforms that blend manual judgment with TradingView webhook automation.
Interesting Read: Hey Traders! Multiply Your Trades, Not Your Effort with Smart Multipliers
How Does Algo Trading Work Step-by-Step?

Think in loops, not isolated trades:
- Signals Your “if-this-then-that.” Examples: price breaks yesterday’s high with volume; 20EMA crosses 50EMA; RSI exits oversold. The key is clarity. If another trader can read your rule and get the same answer you do, it’s rule-ready. In automated trading India, clarity in signals ensures that TradingView webhooks trigger only valid conditions.
- Risk rules Before any entry, define sizing and protection:
- Position sizing (fixed lot, % of equity, or volatility-adjusted)
- SL/TP templates (initial stop, take-profit, trailing conditions)
- MTM caps (daily loss cap, daily profit lock rules) Risk rules are the “seatbelts” of algo trading. They don’t make you faster; they keep you from flying through the windshield. Learn more about MTM - Understand your profit or loss, live.
- Order routing (where supported) A signal alone does nothing. You need a path from signal → execution at your broker. Some workflows keep you fully manual (you click). Others use an execution layer to translate a rule or an alert into an order your broker can accept. Whether manual or automated, the objective is the same: reduce friction and apply the same rules every time.
If your workflow uses TradingView webhooks, alerts can reach your broker in milliseconds, crucial for algo trading India users focused on speed.Read: TradingView To Broker Execution: The Proven Algo Secret
- Logs & review If you can’t audit what happened - time, symbol, price, rule fired, risk applied - you’ll struggle to improve. Good workflows capture enough detail to answer: What did we do? Why? Did it follow the rules? What breaks when the regime changes?
What Is a TradingView Webhook and Why Does It Matter in India?
From TradingView alerts to execution (conceptual, platform-neutral).
A common starting point for retail traders is TradingView alerts.
What is a webhook?
A webhook is a small HTTP message that one app sends to another when an event happens. In this context, TradingView can send an alert (your signal) to an execution layer that, where supported, can validate and route an order to your broker.
Typical steps (high-level):
- Define your alert condition in TradingView.
- Configure the alert to send a webhook to your chosen endpoint.
- The endpoint validates the payload (symbol, side, qty, key).
- If checks pass, it prepares an order request to the broker (where supported).
- You receive a success/fail response and a log entry.
The best algo trading software in India simplifies this pipeline with built-in endpoints.
How to Test Your Algo Trading Setup Before Going Live?

- Dry-run first. Most failures are wiring issues: wrong symbol, quantity field, or a missing token.
- Add safety checks. Time filters, max qty per signal, and “cool-down” windows reduce accidental spam.
- Separate intent from execution. Your signal logic shouldn’t need to know how orders are placed; that’s the execution layer’s job.
This guide is platform-neutral. Always follow your broker’s current policies and your tool’s documentation. Examples are illustrative only.
Risks & guardrails (read this twice): What Are the Risks of Automated Trading in India?
Algo trading is less about clever signals and more about operational discipline. The major risks:
- Latency & slippage Markets move. Between signal and fill, prices change. Reduce friction in your workflow and avoid “over-automation” that adds hops you don’t need. For manual traders, a single well-designed action can be quicker than a slow automation chain.
- Overfitting & regime change A backtest that looks perfect usually learned past noise. Keep rules simple. Prefer concepts that survive across regimes (volatility filters, time-based stops, risk caps). Re-validate when conditions change.
- Integration failures Webhooks can fail. APIs return errors. Brokers throttle. Design circuit breakers: if you get repeated errors or unexpected fills, auto-halt your system and fall back to manual.
- Operational hygiene Use checklists. Verify account selection before market open. Confirm market status (regular session vs special). Make sure your logs capture enough detail to reconstruct any day.
SEBI & compliance basics (educational only)
Regulatory treatment of automation evolves. Brokers may differ in how they enable retail automation and what they allow. As a retail trader, stay aligned with:
- Your broker’s latest guidance on automation and API usage.
- Your tool’s documentation for supported behaviors and limits.
- Good record-keeping (logs), which helps you review what actually ran.
This article does not give legal, tax, or investment advice. It’s an educational overview of concepts used by traders to systemize their workflows.
How to Choose the Best Algo Trading Software or Platform in India?
Picking an algo trading platform: a practical checklist
Choosing tools is less about features and more about your workflow. Use this checklist to compare options without getting lost in jargon.
Core criteria (rank them 1–5 for your needs):
How to use it: pick three platforms, run this table line-by-line, and write notes. You’ll see quickly which tool fits your algo trading workflow today, and which one you can grow into.
Three simple strategy examples (illustrative, platform-neutral)
These are conceptual examples to show how rules translate into action. Adapt to your risk and broker constraints. Backtest and dry-run before live. Educational only.
1) Breakout + time stop (intraday)
- Intent: Enter strength. Get out if it doesn’t go soon.
- Signal (if/then): If price breaks yesterday’s high with ≥X% volume above 20-day average, go long.
- Sizing: Fixed lot or risk-per-trade (e.g., 0.5% of equity).
- Initial SL: Below breakout candle low or a fixed ATR multiple.
- TP: Partial at +1R. Trail remainder with a structure-based stop (e.g., last swing low).
- Time stop: If price doesn’t move +0.5R within 20 minutes, exit market.
- Guardrails: Trade only between 9:25–14:45. Max N trades/day. Daily MTM cap.
Why it works (when it works): Strong days often move early. Time stop cuts “dead air” and preserves attention.
2) MA cross + partial exits (swing or intraday)
- Signal: 20EMA crosses above 50EMA. Price above VWAP if intraday.
- Sizing: Volatility-adjusted (e.g., fewer lots when ATR is high).
- Initial SL: Below recent swing or x*ATR.
- TP: Scale out 30% at +1R, 30% at +2R. Trail the rest under 20EMA.
- Guardrails: No trades on event days you avoid. Stop new entries after daily MTM cap hit.
Why it works (when it works): Trend days or quiet trend weeks. Partial exits bank progress and reduce regret.
3) Opening range fade + risk cap (advanced intraday)
- Signal: In the first 20 minutes, if the price expands by more than k× the average opening range and shows exhaustion (e.g., a lower high for longs fades), take a counter-move with a small size.
- Sizing: Tiny by default; only add if volatility falls back into normal bands.
- SL: Hard stop beyond the extreme. No widen.
- TP: Mean reversion to VWAP or midpoint of the opening range.
- Guardrails: Strict daily loss cap. No re-entry after SL. Auto-halt if VIX-like proxy spikes.
Why it works (when it works): Some opens overshoot. The rule is as much about not adding to losers as it is about entries.
Note: These examples are not recommendations. Markets change. Validate on your data, respect your broker’s policies, and keep risk small.
FAQs (clear, concise)

Q1) What is algo trading in simple words? A rules-based way to trade. You define entry, exit, and risk rules. You can click them manually, automate some parts, or automate end-to-end where supported.
Q2) Do I need to code to do algo trading? Not necessarily. Many traders use no-code building blocks and TradingView webhooks to trigger rules. Others still click entries manually and automate only risk and logging.
Q3) Is fully automated trading always better than manual? No. Automation brings consistency. Manual brings context. Many traders run a hybrid: manual entries + automated risk templates and audit logs.
Q4) How do TradingView webhooks fit in? TradingView can send an alert (your signal) to an execution endpoint. That endpoint validates the payload and, where supported, routes orders to your broker. Always dry-run and add safety checks.
Q5) Why do people talk about latency and slippage in algo trading? Because between a signal and a fill, the price can move. Reducing steps, handling errors, and keeping your workflow simple helps reduce slippage. There’s no way to eliminate it entirely.
Q6) What should I log for review? Timestamp, symbol, side, qty, price, the rule that fired, risk state (e.g., MTM cap hit), and any errors/cancellations. Logs turn guesswork into learning.
Q7) Is algo trading legal for retail traders in India? Rules evolve. Follow your broker’s latest policies and your tool’s documentation. Maintain good records. This guide is not legal advice.
Q8) How big should I start? Smaller than you think. Prove the loop (signal → risk → execution → log) in a dry-run or tiny-size mode before scaling.
Interesting Read: How Groww Users Can Now Unlock Algo Trading with Cirrus: Step-by-Step Guide
Glossary (short, useful)
- Algo trading: Trading with predefined rules for entries, exits, and risk.
- Automation: Software executes parts or all of your rules.
- Hybrid: Manual discretion plus automated guardrails.
- Signal: The condition that says “act now.”
- Risk rules: Position sizing, SL/TP templates, MTM caps, time windows.
- Execution layer: The component that turns intent into broker-compatible orders (where supported).
- Webhook: A small HTTP message sent when an event occurs (e.g., an alert firing).
- Payload: The data inside a webhook (symbol, side, qty, etc.).
- Latency: Time between signal and execution.
- Slippage: Difference between expected and actual fill price.
- MTM (mark-to-market): Real-time P&L used for daily caps.
- Audit log: Record of actions and outcomes for later review.
Platform checklist
Use this 10-point quick scan when evaluating algo trading tools:
- Does it work for manual and automated flows?
- Are risk rules clear and easy to apply?
- Is account selection obvious to prevent mistakes?
- Are TradingView webhooks documented with examples?
- Can I dry-run or limit size easily?
- Are logs detailed and exportable?
- Is broker support documented (where supported)?
- Are errors visible, with safe circuit breakers?
- Is pricing transparent?
- Is there real, up-to-date education?

Conclusion: Why Making Algo Trading Boring Is the Real Goal
Make algo trading boring (that’s a compliment)
Great systems feel uneventful. You know your rules. You know what happens when they fire. You know where to look when something breaks. Whether you trade manually, automate parts, or go full-auto where supported, the winning habit is the same: build a simple loop you can repeat - signal, risk, execution, logs - then improve it one variable at a time.
Next steps
- Read the TradingView → execution how-to (webhook basics, testing).
- Compare platforms with the checklist above and pick the one that fits your workflow.
- Start tiny. Dry-run first. Keep logs. Iterate.
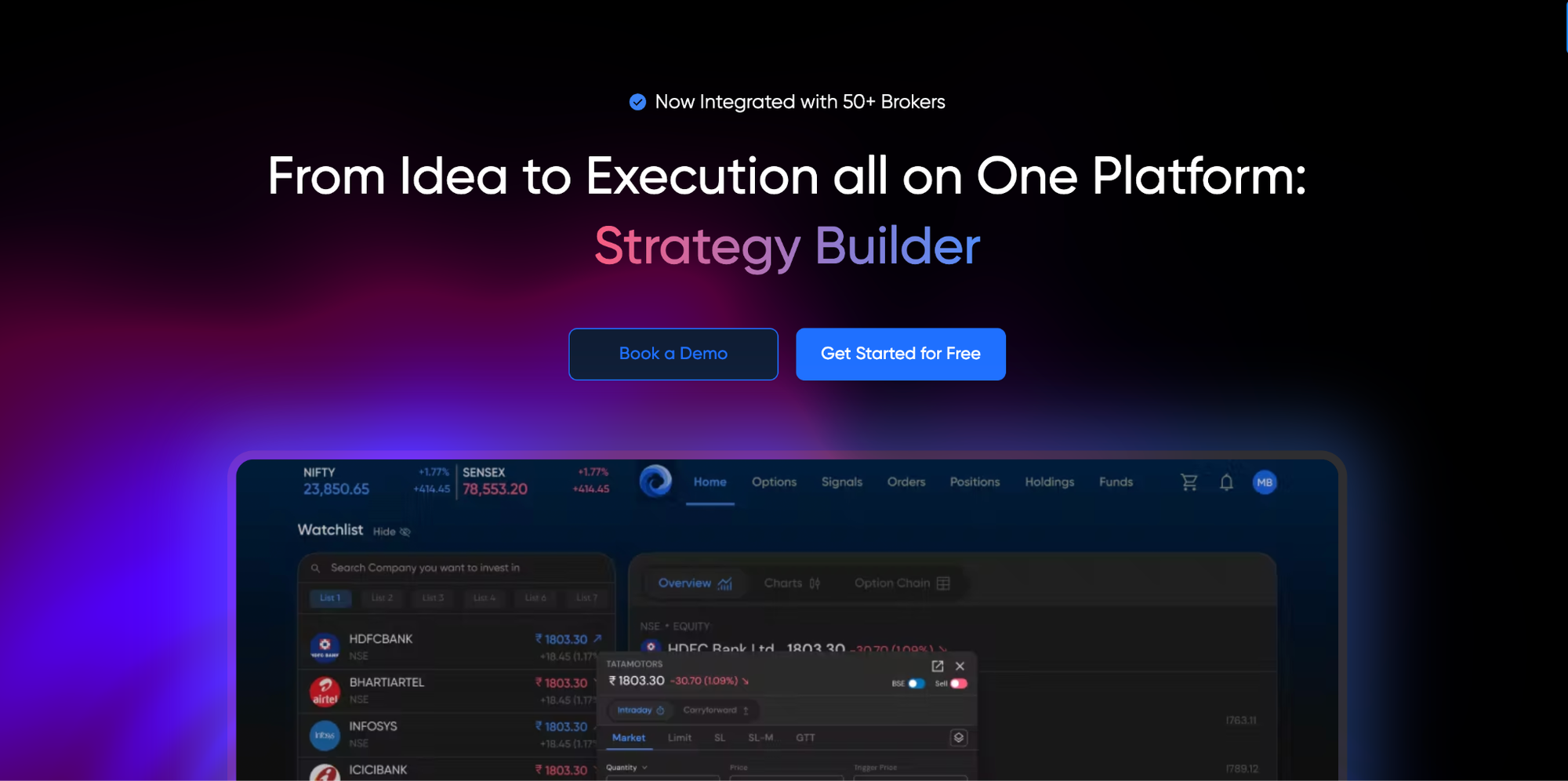
See a centralized execution workflow
Disclaimer
This article is for educational purposes only and is not investment advice or a recommendation. Trading involves risk of loss. Examples and screenshots are illustrative. Regulatory views may evolve; always follow your broker’s and regulator’s guidance.






